两点之间如何连线?
众所周知,两个点之间连线有以下几种方式:
- 通过直接连接;
- 通过折线连接;
- 通过曲线连接。
直线与拆线连接这两种方式很简单,今天我们这里讨论的是如何通过曲线来连接两个点。
在 JavaScript 中,绘制图形通常会使用到 canvas 或是 svg,考虑到后续会进行一些 DOM 操作,我们使用 svg 来实现接下来的案例。
svg 绘制曲线有三种方式,其中两个用来绘制贝塞尔曲线,另外一种用来绘制弧形或者说是圆的一部分。
两点之间通过曲线连接
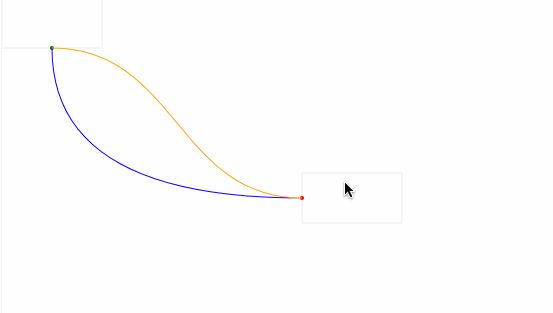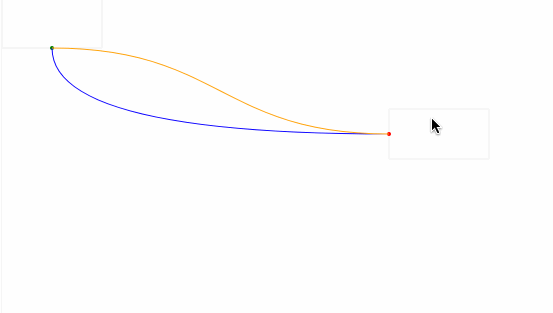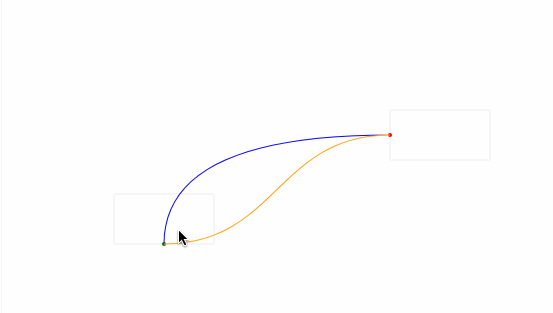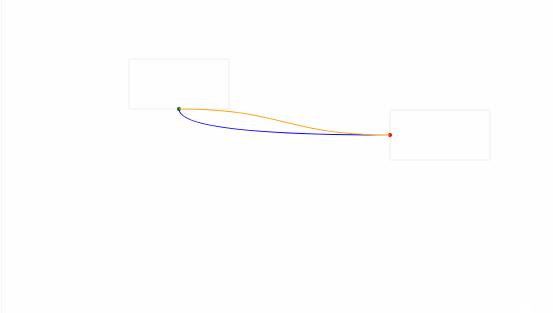
接下来进入正题。给出两个点:(50,50) 和 (300,200),然后使用曲线形式连接:
html
<svg
width="600"
height="400"
viewBox="0 0 600 400"
>
<g name="points">
<circle
cx="50"
cy="50"
r="2"
fill="green"
/>
<circle
cx="300"
cy="200"
r="2"
fill="red"
/>
</g>
<g name="curves">
<path
d="
M 50 50
Q 50 200 300 200
"
stroke="blue"
fill="none"
/>
<path
d="
M 50 50
C 250 0, 200 200, 300 200
"
stroke="orange"
fill="none"
/>
</g>
</svg>
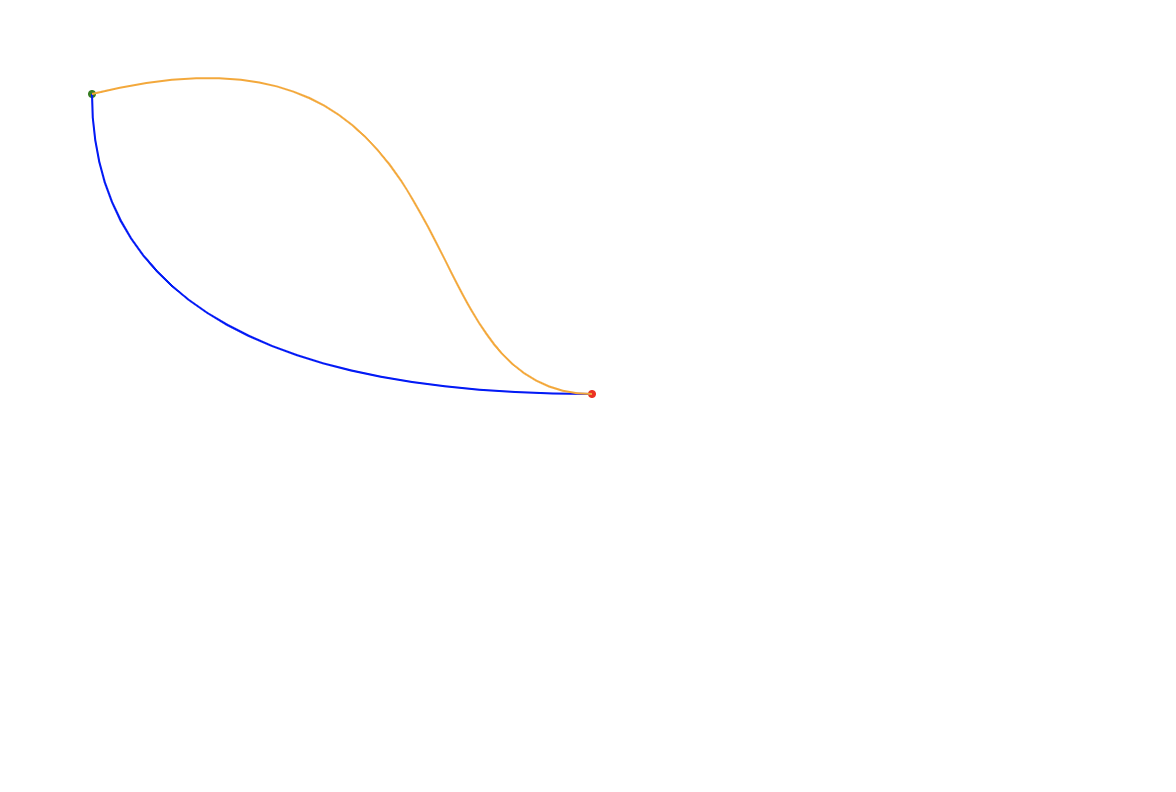
如上图所示,蓝色的是通过二次贝塞尔曲线绘制而成,它的起点是 (50,50),终点是 (300, 200),控制点是 (50,200);橙色的则是通过三次贝塞尔绘制而成,它的起点和终点与蓝色曲线一样,两个控制点分别为 (250,0) 和 (200,200)。
动态计算控制点
接下来我们使用代码动态计算控制点:
vue
<template>
<div style="width: 600px; height: 400px; margin: 50px auto; border: 1px solid #f1f1f1">
<svg
width="600"
height="400"
viewBox="0 0 600 400"
>
<g name="points">
<g
v-for="item of points"
:key="item.name"
name="start-point"
:transform="`translate(${item.translate.x},${item.translate.y})`"
@mousedown="handleMouseDown(item.name, $event)"
>
<rect
width="100"
height="50"
fill="#fff"
stroke="#eee"
/>
<circle
:cx="item.x"
:cy="item.y"
r="2"
:fill="item.fill"
/>
</g>
</g>
<g name="curves">
<path
v-for="item of curves"
:key="item.name"
:d="item.path"
:stroke="item.stroke"
fill="none"
/>
</g>
</svg>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed, ref } from 'vue'
const currentPoint = ref<any>(null)
const coordinate = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 })
const startPoint = ref({
name: 'start',
translate: {
x: 0,
y: 0
},
x: 50,
y: 50,
fill: 'green'
})
const endPoint = ref({
name: 'end',
translate: {
x: 300,
y: 175
},
x: 0,
y: 25,
fill: 'red'
})
const points = computed(() => {
return [
startPoint.value,
endPoint.value
]
})
const x1 = computed(() => startPoint.value.translate.x + startPoint.value.x)
const y1 = computed(() => startPoint.value.translate.y + startPoint.value.y)
const x2 = computed(() => endPoint.value.translate.x + endPoint.value.x)
const y2 = computed(() => endPoint.value.translate.y + endPoint.value.y)
const quadraticBezierCurve = computed(() => {
return {
name: 'quadraticBezierCurve',
path: `
M ${x1.value} ${y1.value}
Q ${x1.value} ${y2.value}, ${x2.value} ${y2.value}
`,
stroke: 'blue'
}
})
const cubicBezierCruve = computed(() => {
const cpx1 = x1.value + (x2.value - x1.value) / 2
const cpy1 = y1.value
const cpx2 = cpx1
const cpy2 = y2.value
return {
name: 'cubicBezierCruve',
path: `
M ${x1.value} ${y1.value}
C ${cpx1} ${cpy1}, ${cpx2} ${cpy2}, ${x2.value} ${y2.value}
`,
stroke: 'orange'
}
})
const curves = computed(() => {
return [
quadraticBezierCurve.value,
cubicBezierCruve.value
]
})
const handleMouseDown = (name: String, e: MouseEvent) => {
e.preventDefault()
currentPoint.value = name === 'start'
? startPoint.value
: endPoint.value
coordinate.value.x = e.clientX
coordinate.value.y = e.clientY
document.addEventListener('mousemove', handleMouseMove, false)
document.addEventListener('mouseup', handleMouseUp, false)
}
const handleMouseMove = (e: MouseEvent) => {
const { clientX, clientY } = e
currentPoint.value.translate.x += (clientX - coordinate.value.x)
currentPoint.value.translate.y += (clientY - coordinate.value.y)
coordinate.value.x = clientX
coordinate.value.y = clientY
}
const handleMouseUp = (e: MouseEvent) => {
e.preventDefault()
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', handleMouseMove, false)
document.removeEventListener('mousedown', handleMouseUp, false)
coordinate.value = { x: 0, y: 0 }
currentPoint.value = null
}
</script>
如上面的代码所示,在 quadraticBezierCurve 这个计算属性中,我们实现了二次贝塞尔曲线的控制点的计算,也就是使用了起始点的 x 坐标以及结束点的 y 坐标 (x1, y2),动态生成曲线。
而在 cubicBezierCruve 这个计算属性中,我们将两个控制点的 x 坐标设置为起始点与结束点之间的中点,y 坐标则分别取了 y1 与 y2。
最后,我们给起始坐标和结束坐标增加了拖拽事件处理,实现了通过曲线的形式动态地连接两个坐标点,如下图所示:
动态计算起始点
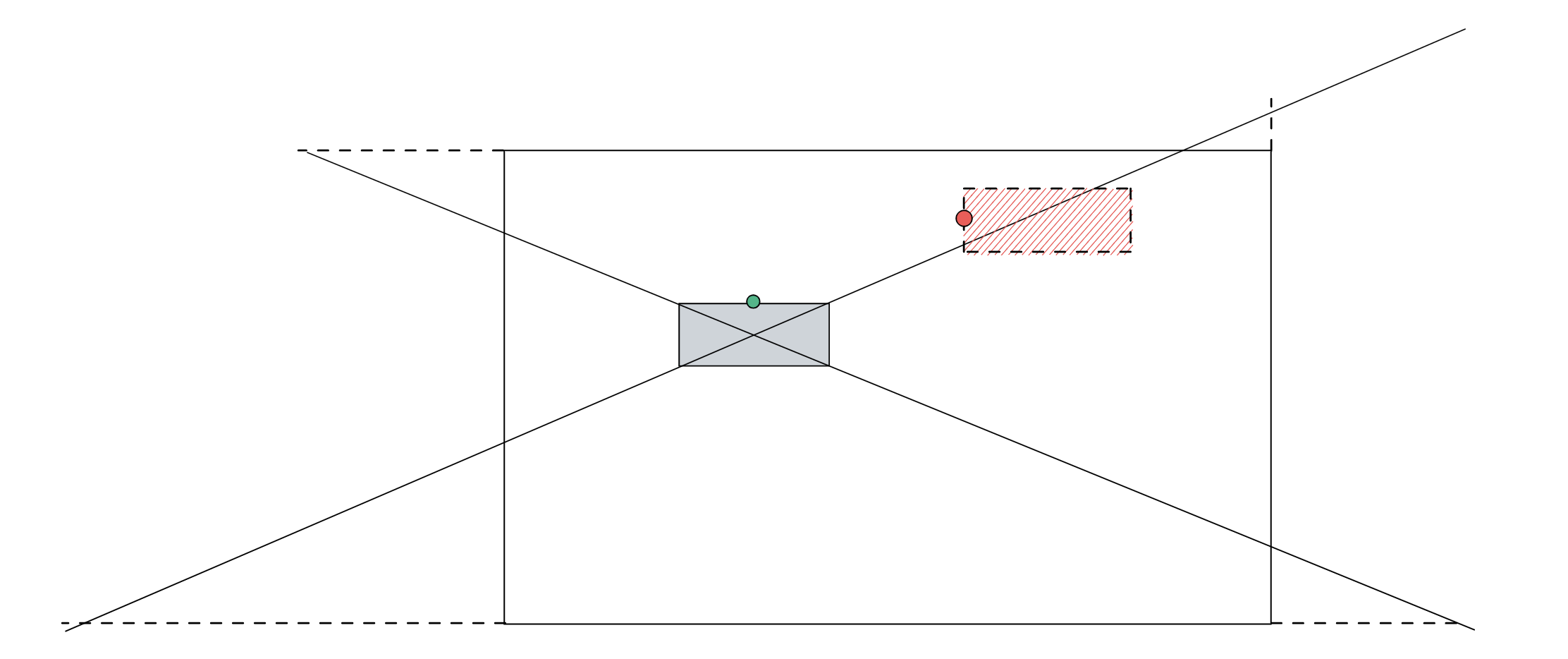
在上面的例子,我们实现了动态去计算控制点的坐标,在示例图中,可以看到曲线有穿透矩形的问题,接下来通过动态计算控制点来解决这个问题。
如下图所示,当另外一个正在移动的点(红色矩形)进入三角形区域中(固定矩形与画板相交的四个方向的三角形)时,我们动态改变固定矩形(灰色)的出发点位置:
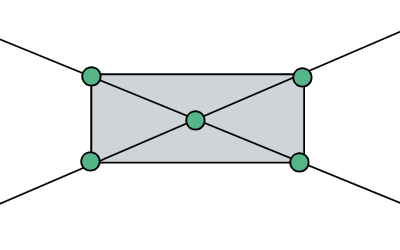
接下来我们用代码来获取这些三角形位置:
首先我们可以确定的是矩形的中点与四个顶点组成的四个方位的三角形:
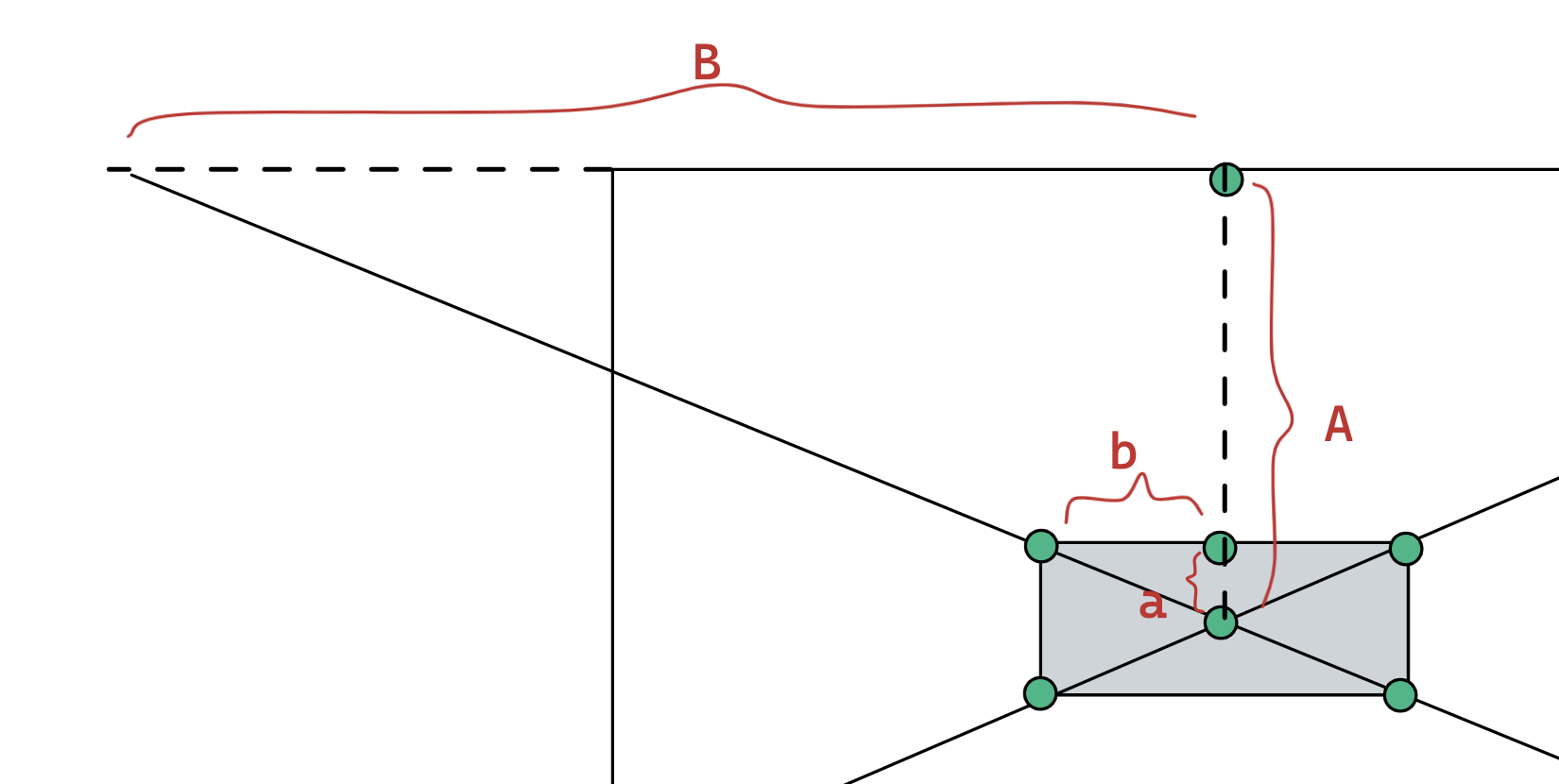
接下来以上面的三角形为例,从下图可以看出,相似三角形的连长比是一致的,也就是说:a : A = b : B,通过这个特性,我们可以求出外三角形三个点的坐标。
如下面代码所示:
ts
function getCentralPoint (
pos: Rect['allowPoints'][number],
vertexes: RectVertexes
): Point {
const [tl, tr, bl, br] = vertexes
let x = 0
let y = 0
switch (pos) {
case 'top':
x = tl.x + (tr.x - tl.x) / 2
y = tr.y
break
case 'right':
x = tr.x
y = tr.y + (br.y - tr.y) / 2
break
case 'bottom':
x = bl.x + (br.x - bl.x) / 2
y = br.y
break
case 'left':
x = tl.x
y = tl.y + (bl.y - tl.y) / 2
break
default:
break
}
return {
x,
y
}
}
function getTriangle (
pos: Rect['allowPoints'][number],
vertexes: RectVertexes,
cp: Point,
wrapperSize: Size
): Triangle {
const sideCentralPoint = getCentralPoint(pos, vertexes)
// 计算底边长度
if (['top', 'bottom'].includes(pos)) {
const rate = pos === 'top'
? Math.abs(cp.y - sideCentralPoint.y) / cp.y
: Math.abs(cp.y - sideCentralPoint.y) / (wrapperSize.height - cp.y)
const lSideLength = Math.abs(cp.x - vertexes[0].x) / rate
const rSideLength = Math.abs(cp.x - vertexes[1].x) / rate
// 左侧点 x y
const lx = cp.x - lSideLength
const ly = pos === 'top' ? 0 : wrapperSize.height
// 右侧点 x y
const rx = rSideLength + cp.x
const ry = ly
return [
{ x: lx, y: ly },
{ x: rx, y: ry },
{ ...cp }
]
} else {
const rate = pos === 'right'
? Math.abs(cp.x - sideCentralPoint.x) / (wrapperSize.width - cp.x)
: Math.abs(cp.x - sideCentralPoint.x) / cp.x
const tSideLength = Math.abs(cp.y - vertexes[0].y) / rate
const bSideLength = Math.abs(cp.y - vertexes[2].y) / rate
// 上侧点 x y
const tx = pos === 'left' ? 0 : wrapperSize.width
const ty = cp.y - tSideLength
// 下侧点 x y
const bx = tx
const by = bSideLength + cp.y
return [
{ x: tx, y: ty },
{ x: bx, y: by },
{ ...cp }
]
}
}
export default (
rect: Ref<Rect>,
wrapperSize: Size
) => {
// 获取四个三角形
const triangles = computed(() => {
const {
translate: {
x,
y
},
width,
height,
allowPoints
} = rect.value
// 矩形四个顶点
// top-left top-right
// bottom-left bottom-right
const vertexes: RectVertexes = [
{ x, y },
{ x: x + width, y },
{ x, y: y + height },
{ x: x + width, y: y + height }
]
// 矩形中点
const cp: Point = {
x: x + width / 2,
y: y + height / 2
}
const triangles: Triangles = {
top: null,
right: null,
bottom: null,
left: null
}
allowPoints.forEach(pos => {
triangles[pos] = getTriangle(
pos,
vertexes,
cp,
wrapperSize
)
})
return triangles
})
return {
triangles
}
}
通过上面的代码,我们就计算出了四个方位的三角形,效果如下图所示:
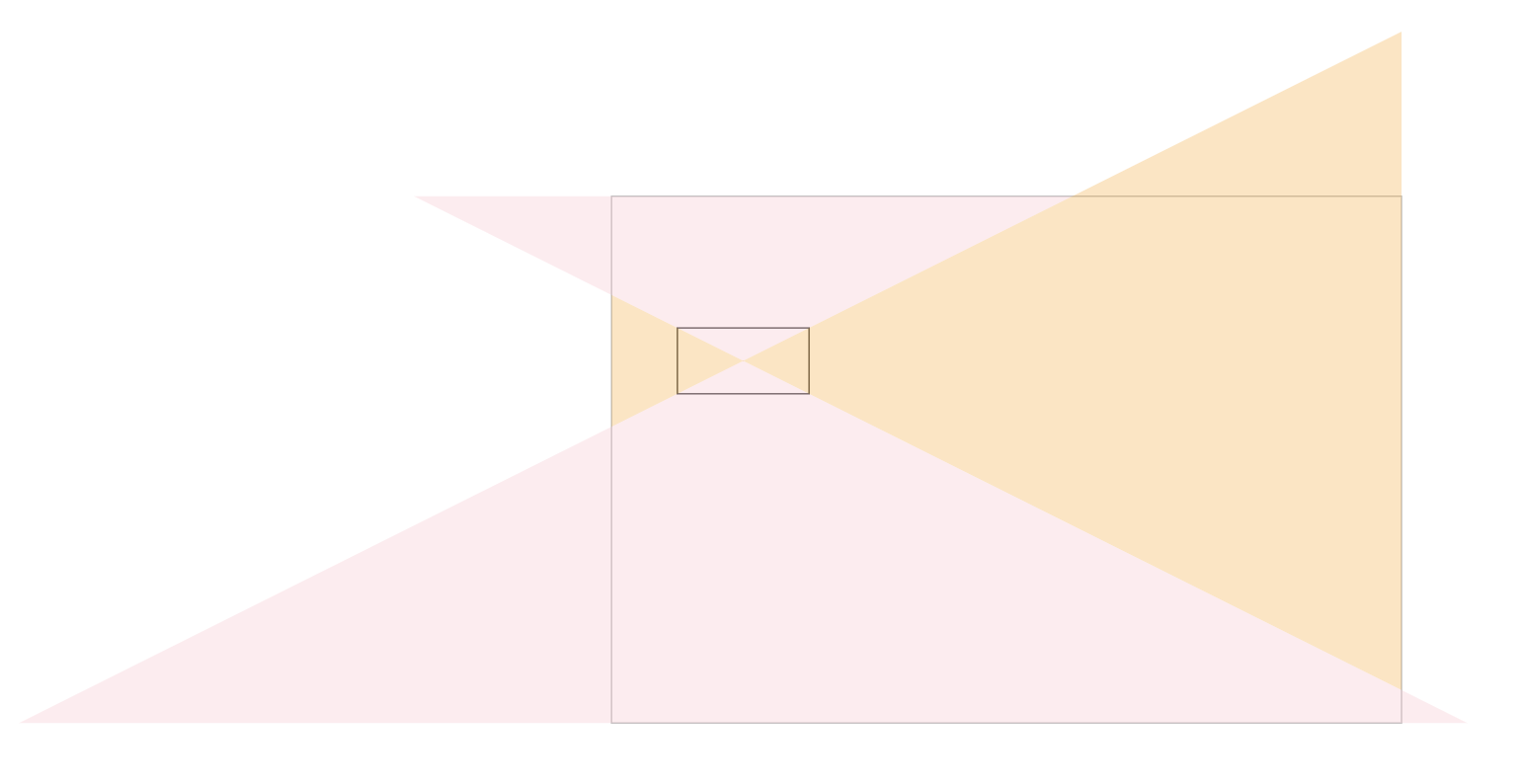
判断点位于三角形内部
现在压力来到了如何判断某个点进入了该三角形区域了。这里需要用到向量的知识:当一个点它位于由三角形的三条边的向量的同一侧时,则说明它在该三角形内部。
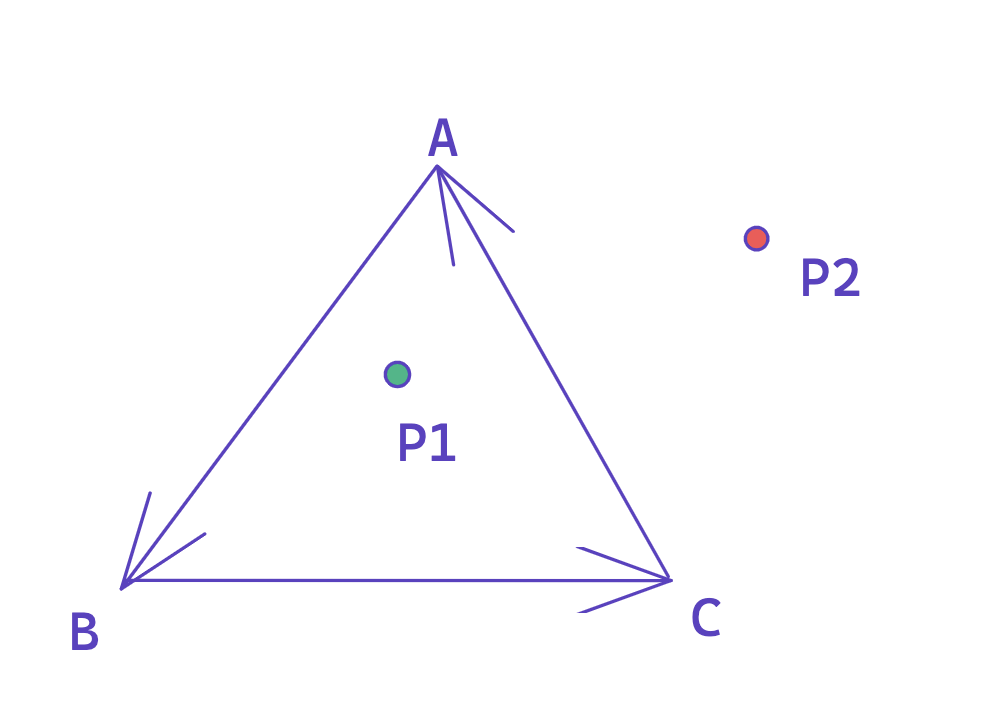
如上图所示,点 P1 位于向量 AB、向量 BC、向量 CA 的左侧,这说明点 P1 处于三角形 ABC 的内部;而点 P2 位于向量 AB、向量 BC 的左侧,却位于向量 CA 的右侧,说明点 P2 不在三角形的内部。
接下来,我们用代码来实现这一个算法,这里会利用到叉乘来处理,它具有方向性。对于下图中的三角形 ABC 与点 P1,使用 向量 P1A x 向量 P1B,如果向量在 P1A 在向量 P1B 的左侧,则结果大于 0,否则结果小于 0;向量 P1B x 向量 P1C 与 向量 P1C x 向量 P1A 同理。如果三者计算都大于 0,则说明点 P1 位于三角形 ABC 的内部。
ts
// 向量
const vec = (a: Point, b: Point): Point => {
return {
x: b.x - a.x,
y: b.y - a.y
}
}
// 叉乘函数
const vecProduct = (v1: Point, v2: Point) => v1.x * v2.y - v2.x * v1.y
const sameSymbols = (a: number, b: number) => (a ^ b) >= 0
/**
* 判断某个点是否在三角形内部
* 点位于三角形三条边的同一侧
* @param triangle
* @param point
*/
export const isPointInTriangle = (triangle: Triangle, point: Point) => {
const PA = vec(point, triangle[0])
const PB = vec(point, triangle[1])
const PC = vec(point, triangle[2])
const R1 = vecProduct(PA, PB)
const R2 = vecProduct(PB, PC)
const R3 = vecProduct(PC, PA)
return sameSymbols(R1, R2) && sameSymbols(R2, R3)
}

动态计算起点
如下面的代码所示:
vue
<template>
<div>
<svg
width="1000"
height="800"
viewBox="0 0 1000 800"
>
<g
name="outline"
transform="translate(200, 200)"
>
<g
name="triangles"
v-for="(item, index) of effectiveTriangles"
:key="index"
>
<path
:d="`
M ${item[0].x} ${item[0].y}
L ${item[1].x} ${item[1].y}
L ${item[2].x} ${item[2].y}
Z
`"
:fill="index % 2 === 0 ? 'pink' : 'orange'"
opacity="0.3"
/>
</g>
<rect
v-bind="wrapperSize"
stroke="#bbb"
fill="none"
/>
<g
name="rect"
:transform="`translate(${rect.translate.x}, ${rect.translate.y})`"
>
<rect
:width="rect.width"
:height="rect.height"
stroke="#333"
fill="none"
/>
<circle
:cx="rect.point.x"
:cy="rect.point.y"
r="10"
fill="green"
stroke="none"
/>
</g>
<g
name="other-rect"
:transform="`translate(${otherRect.translate.x}, ${otherRect.translate.y})`"
@mousedown="handleMouseDown"
>
<rect
:width="otherRect.width"
:height="otherRect.height"
stroke="#333"
fill="#fff"
/>
<circle
:cx="otherRect.point.x"
:cy="otherRect.point.y"
r="10"
fill="red"
stroke="none"
/>
</g>
</g>
</svg>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed, ref, watch } from 'vue'
import { Point, Rect, Size, Triangle } from '.'
import useTriangle from './composables/useTriangle'
import { isPointInTriangle } from './utils/tools';
const wrapperSize: Size = {
width: 600,
height: 400
}
const rect = ref<Rect>({
name: 'rect',
translate: {
x: 50,
y: 100
},
width: 100,
height: 50,
allowPoints: ['top', 'right', 'bottom', 'left'],
point: {
x: 50,
y: 50
}
})
const otherRect = ref<Rect>({
name: 'rect',
translate: {
x: 50,
y: 300
},
width: 100,
height: 50,
allowPoints: ['top', 'right', 'bottom', 'left'],
point: {
x: 50,
y: 0
}
})
const {
triangles
} = useTriangle(rect, wrapperSize)
const effectiveTriangles = computed<Triangle[]>(() => {
return Object.values(triangles.value).filter(Boolean)
})
watch(() => otherRect.value.translate, () => {
const p = {
x: otherRect.value.translate.x + otherRect.value.point.x,
y: otherRect.value.translate.y + otherRect.value.point.y
}
if (triangles.value.top && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.top, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: rect.value.width / 2,
y: 0
}
} else if (triangles.value.right && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.right, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: rect.value.width,
y: rect.value.height / 2
}
} else if (triangles.value.bottom && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.bottom, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: rect.value.width / 2,
y: rect.value.height
}
} else if (triangles.value.left && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.left, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: 0,
y: rect.value.height / 2
}
}
}, {
immediate: true,
deep: true
})
const coordinate = ref<Point>({ x: 0, y: 0 })
const handleMouseDown = (e: MouseEvent) => {
e.preventDefault()
coordinate.value.x = e.clientX
coordinate.value.y = e.clientY
document.addEventListener('mousemove', handleMouseMove, false)
document.addEventListener('mouseup', handleMouseUp, false)
}
const handleMouseMove = (e: MouseEvent) => {
const { clientX, clientY } = e
otherRect.value.translate.x += (clientX - coordinate.value.x)
otherRect.value.translate.y += (clientY - coordinate.value.y)
coordinate.value.x = clientX
coordinate.value.y = clientY
}
const handleMouseUp = (e: MouseEvent) => {
e.preventDefault()
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', handleMouseMove, false)
document.removeEventListener('mousedown', handleMouseUp, false)
coordinate.value = { x: 0, y: 0 }
}
</script>
结果如下图:
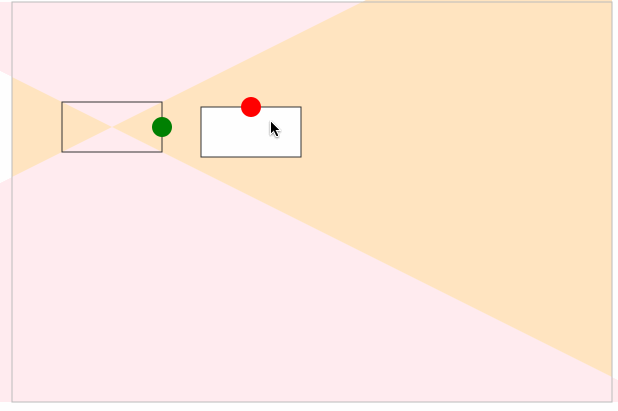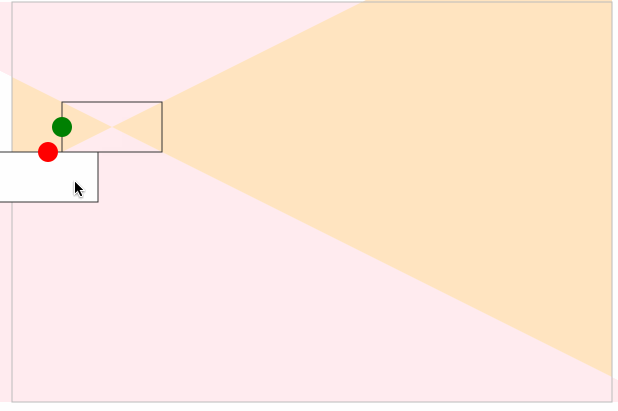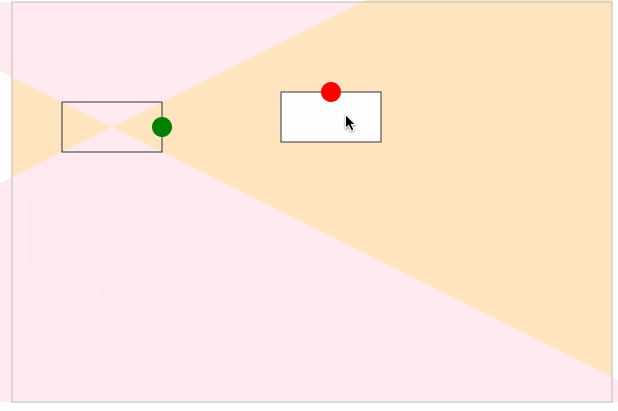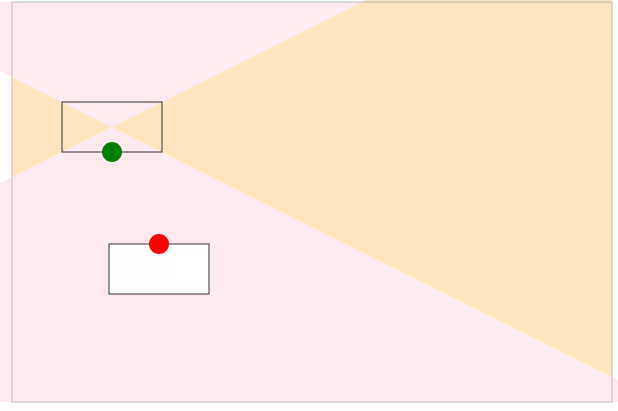
动态计算结束点
当起点被确定下来之后,以同样的方式,把结束点也确定下来。增加以下代码
diff
<template>
<div>
<svg
width="1000"
height="800"
viewBox="0 0 1000 800"
>
<g
name="outline"
transform="translate(200, 200)"
>
<!-- <g
name="triangles"
v-for="(item, index) of effectiveTriangles"
:key="index"
>
<path
:d="`
M ${item[0].x} ${item[0].y}
L ${item[1].x} ${item[1].y}
L ${item[2].x} ${item[2].y}
Z
`"
:fill="index % 2 === 0 ? 'pink' : 'orange'"
opacity="0.3"
/>
</g> -->
<g
name="other-rect-triangles"
v-for="(item, index) of otherRectEffectiveTriangles"
:key="index"
>
<path
:d="`
M ${item[0].x} ${item[0].y}
L ${item[1].x} ${item[1].y}
L ${item[2].x} ${item[2].y}
Z
`"
:fill="index % 2 === 0 ? 'green' : 'blue'"
opacity="0.1"
/>
</g>
<rect
v-bind="wrapperSize"
stroke="#bbb"
fill="none"
/>
<g
name="rect"
:transform="`translate(${rect.translate.x}, ${rect.translate.y})`"
>
<rect
:width="rect.width"
:height="rect.height"
stroke="#333"
fill="none"
/>
<circle
:cx="rect.point.x"
:cy="rect.point.y"
r="10"
fill="green"
stroke="none"
/>
</g>
<g
name="other-rect"
:transform="`translate(${otherRect.translate.x}, ${otherRect.translate.y})`"
@mousedown="handleMouseDown"
>
<rect
:width="otherRect.width"
:height="otherRect.height"
stroke="#333"
fill="#fff"
/>
<circle
:cx="otherRect.point.x"
:cy="otherRect.point.y"
r="10"
fill="red"
stroke="none"
/>
</g>
</g>
</svg>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed, ref, watch } from 'vue'
import { Point, Rect, Size, Triangle } from '.'
import useTriangle from './composables/useTriangle'
import { isPointInTriangle } from './utils/tools';
const wrapperSize: Size = {
width: 600,
height: 400
}
const rect = ref<Rect>({
name: 'rect',
translate: {
x: 50,
y: 100
},
width: 100,
height: 50,
allowPoints: ['top', 'right', 'bottom', 'left'],
point: {
x: 50,
y: 50
}
})
const otherRect = ref<Rect>({
name: 'rect',
translate: {
x: 50,
y: 300
},
width: 100,
height: 50,
allowPoints: ['top', 'right', 'bottom', 'left'],
point: {
x: 50,
y: 0
}
})
const {
triangles
} = useTriangle(rect, wrapperSize)
+ const {
+ triangles: otherRectTriangles
+ } = useTriangle(otherRect, wrapperSize)
const effectiveTriangles = computed<Triangle[]>(() => {
return Object.values(triangles.value).filter(Boolean)
})
+ const otherRectEffectiveTriangles = computed<Triangle[]>(() => {
+ return Object.values(otherRectTriangles.value).filter(Boolean)
+ })
watch(() => otherRect.value.translate, () => {
const p = {
x: otherRect.value.translate.x + otherRect.value.point.x,
y: otherRect.value.translate.y + otherRect.value.point.y
}
if (triangles.value.top && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.top, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: rect.value.width / 2,
y: 0
}
} else if (triangles.value.right && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.right, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: rect.value.width,
y: rect.value.height / 2
}
} else if (triangles.value.bottom && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.bottom, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: rect.value.width / 2,
y: rect.value.height
}
} else if (triangles.value.left && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.left, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: 0,
y: rect.value.height / 2
}
}
}, {
immediate: true,
deep: true
})
+ watch(() => rect.value.point, () => {
+ const p = {
+ x: rect.value.translate.x + rect.value.point.x,
+ y: rect.value.translate.y + rect.value.point.y
+ }
+ if (otherRectTriangles.value.top && + isPointInTriangle(otherRectTriangles.value.top, p)) {
+ otherRect.value.point = {
+ x: otherRect.value.width / 2,
+ y: 0
+ }
+ } else if (otherRectTriangles.value.right && isPointInTriangle(otherRectTriangles.value.right, p)) {
+ otherRect.value.point = {
+ x: otherRect.value.width,
+ y: otherRect.value.height / 2
+ }
+ } else if (otherRectTriangles.value.bottom && isPointInTriangle(otherRectTriangles.value.bottom, p)) {
+ otherRect.value.point = {
+ x: otherRect.value.width / 2,
+ y: otherRect.value.height
+ }
+ } else if (otherRectTriangles.value.left && isPointInTriangle(otherRectTriangles.value.left, p)) {
+ otherRect.value.point = {
+ x: 0,
+ y: otherRect.value.height / 2
+ }
+ }
+ })
const coordinate = ref<Point>({ x: 0, y: 0 })
const handleMouseDown = (e: MouseEvent) => {
e.preventDefault()
coordinate.value.x = e.clientX
coordinate.value.y = e.clientY
document.addEventListener('mousemove', handleMouseMove, false)
document.addEventListener('mouseup', handleMouseUp, false)
}
const handleMouseMove = (e: MouseEvent) => {
const { clientX, clientY } = e
otherRect.value.translate.x += (clientX - coordinate.value.x)
otherRect.value.translate.y += (clientY - coordinate.value.y)
coordinate.value.x = clientX
coordinate.value.y = clientY
}
const handleMouseUp = (e: MouseEvent) => {
e.preventDefault()
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', handleMouseMove, false)
document.removeEventListener('mousedown', handleMouseUp, false)
coordinate.value = { x: 0, y: 0 }
}
</script>
效果如下图所示:
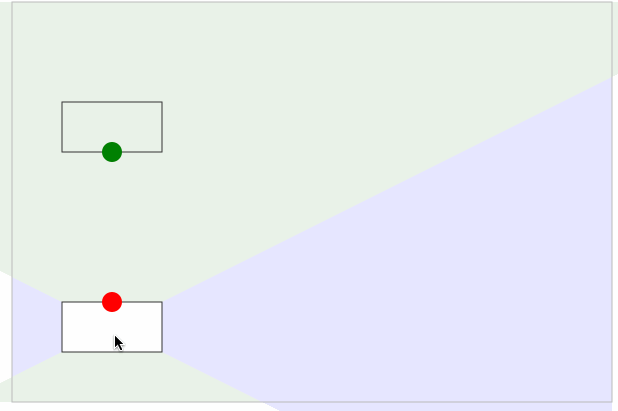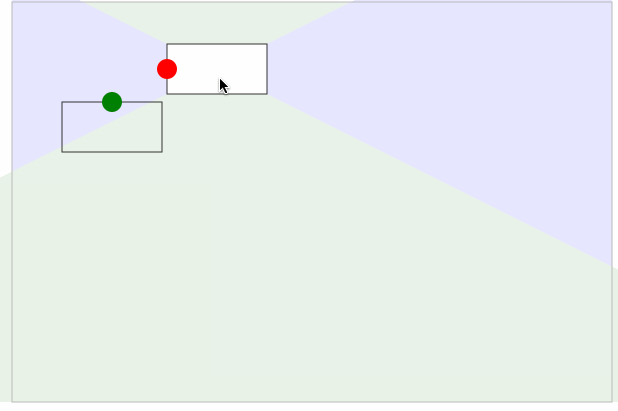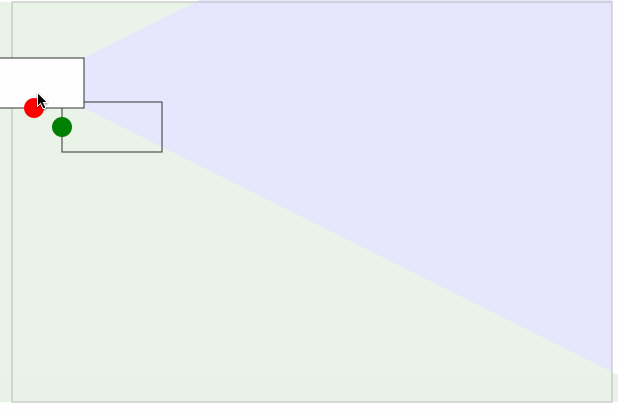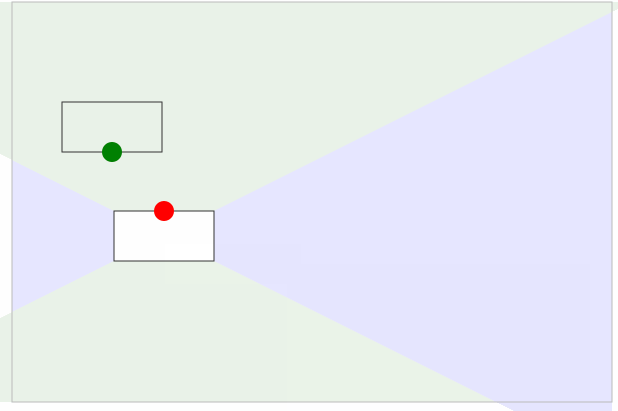
动态连接
最后,只需要在起点和终点之间建立曲线连接即可。效果如下:
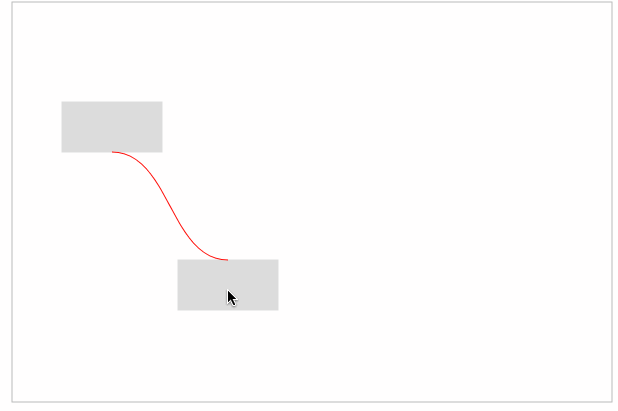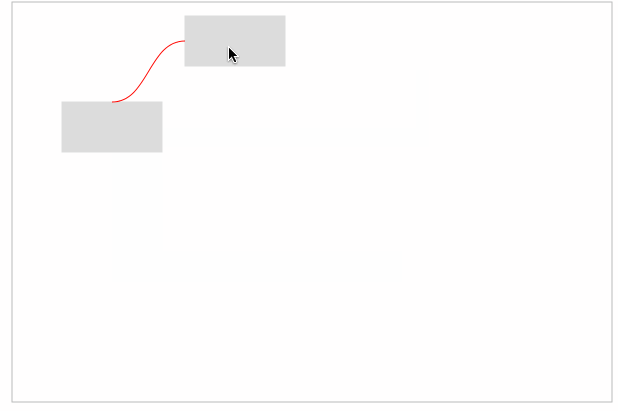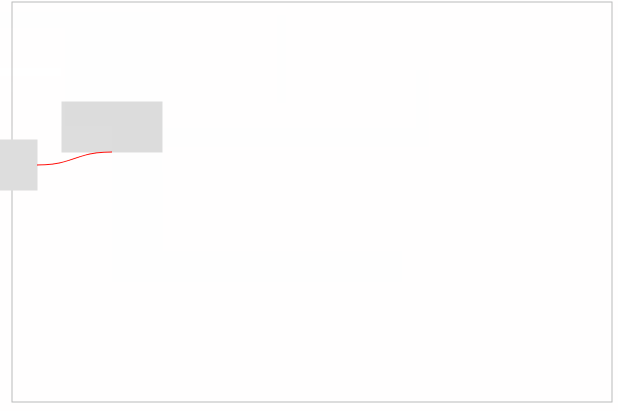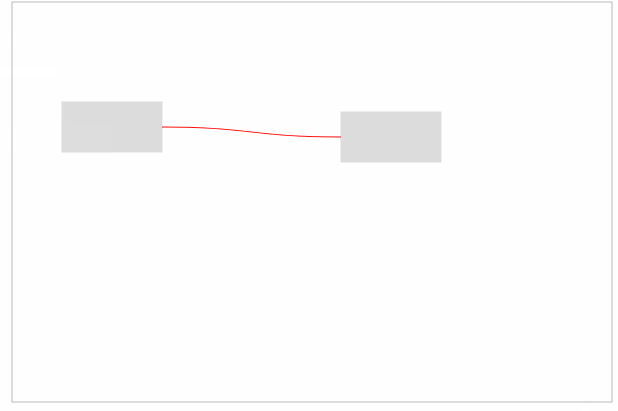
完整代码如下:
src/App.vue
vue
<template>
<div>
<svg
width="1000"
height="800"
viewBox="0 0 1000 800"
>
<g
name="outline"
transform="translate(200, 200)"
>
<rect
v-bind="wrapperSize"
stroke="#bbb"
fill="none"
/>
<g
name="rect"
:transform="`translate(${rect.translate.x}, ${rect.translate.y})`"
>
<rect
:width="rect.width"
:height="rect.height"
stroke="#ddd"
fill="#ddd"
/>
</g>
<g
name="other-rect"
:transform="`translate(${otherRect.translate.x}, ${otherRect.translate.y})`"
@mousedown="handleMouseDown"
>
<rect
:width="otherRect.width"
:height="otherRect.height"
stroke="#ddd"
fill="#ddd"
/>
</g>
<g name="curve-path">
<path
:d="path"
stroke="red"
fill="none"
/>
</g>
</g>
</svg>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed, ref, watch } from 'vue'
import { Point, Rect, Size, Triangle } from '.'
import useTriangle from './composables/useTriangle'
import useCurve from './composables/useCurve'
import { isPointInTriangle } from './utils/tools'
const wrapperSize: Size = {
width: 600,
height: 400
}
const rect = ref<Rect>({
name: 'rect',
translate: {
x: 50,
y: 100
},
width: 100,
height: 50,
allowPoints: ['top', 'right', 'bottom', 'left'],
point: {
x: 50,
y: 50
}
})
const otherRect = ref<Rect>({
name: 'rect',
translate: {
x: 50,
y: 300
},
width: 100,
height: 50,
allowPoints: ['top', 'right', 'bottom', 'left'],
point: {
x: 50,
y: 0
}
})
const {
triangles
} = useTriangle(rect, wrapperSize)
const {
triangles: otherRectTriangles
} = useTriangle(otherRect, wrapperSize)
const {
path
} = useCurve(rect, otherRect)
const effectiveTriangles = computed<Triangle[]>(() => {
return Object.values(triangles.value).filter(Boolean)
})
const otherRectEffectiveTriangles = computed<Triangle[]>(() => {
return Object.values(otherRectTriangles.value).filter(Boolean)
})
watch(() => otherRect.value.translate, () => {
const p = {
x: otherRect.value.translate.x + otherRect.value.point.x,
y: otherRect.value.translate.y + otherRect.value.point.y
}
if (triangles.value.top && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.top, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: rect.value.width / 2,
y: 0
}
} else if (triangles.value.right && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.right, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: rect.value.width,
y: rect.value.height / 2
}
} else if (triangles.value.bottom && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.bottom, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: rect.value.width / 2,
y: rect.value.height
}
} else if (triangles.value.left && isPointInTriangle(triangles.value.left, p)) {
rect.value.point = {
x: 0,
y: rect.value.height / 2
}
}
}, {
immediate: true,
deep: true
})
watch(() => rect.value.point, () => {
const p = {
x: rect.value.translate.x + rect.value.point.x,
y: rect.value.translate.y + rect.value.point.y
}
if (otherRectTriangles.value.top && isPointInTriangle(otherRectTriangles.value.top, p)) {
otherRect.value.point = {
x: otherRect.value.width / 2,
y: 0
}
} else if (otherRectTriangles.value.right && isPointInTriangle(otherRectTriangles.value.right, p)) {
otherRect.value.point = {
x: otherRect.value.width,
y: otherRect.value.height / 2
}
} else if (otherRectTriangles.value.bottom && isPointInTriangle(otherRectTriangles.value.bottom, p)) {
otherRect.value.point = {
x: otherRect.value.width / 2,
y: otherRect.value.height
}
} else if (otherRectTriangles.value.left && isPointInTriangle(otherRectTriangles.value.left, p)) {
otherRect.value.point = {
x: 0,
y: otherRect.value.height / 2
}
}
})
const coordinate = ref<Point>({ x: 0, y: 0 })
const handleMouseDown = (e: MouseEvent) => {
e.preventDefault()
coordinate.value.x = e.clientX
coordinate.value.y = e.clientY
document.addEventListener('mousemove', handleMouseMove, false)
document.addEventListener('mouseup', handleMouseUp, false)
}
const handleMouseMove = (e: MouseEvent) => {
const { clientX, clientY } = e
otherRect.value.translate.x += (clientX - coordinate.value.x)
otherRect.value.translate.y += (clientY - coordinate.value.y)
coordinate.value.x = clientX
coordinate.value.y = clientY
}
const handleMouseUp = (e: MouseEvent) => {
e.preventDefault()
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', handleMouseMove, false)
document.removeEventListener('mousedown', handleMouseUp, false)
coordinate.value = { x: 0, y: 0 }
}
</script>
src/composables/useTriangle.ts
ts
import { Ref, computed } from 'vue'
import { Point, Rect, RectVertexes, Size, Triangle, Triangles } from '..'
function getCentralPoint (
pos: Rect['allowPoints'][number],
vertexes: RectVertexes
): Point {
const [tl, tr, bl, br] = vertexes
let x = 0
let y = 0
switch (pos) {
case 'top':
x = tl.x + (tr.x - tl.x) / 2
y = tr.y
break
case 'right':
x = tr.x
y = tr.y + (br.y - tr.y) / 2
break
case 'bottom':
x = bl.x + (br.x - bl.x) / 2
y = br.y
break
case 'left':
x = tl.x
y = tl.y + (bl.y - tl.y) / 2
break
default:
break
}
return {
x,
y
}
}
function getTriangle (
pos: Rect['allowPoints'][number],
vertexes: RectVertexes,
cp: Point,
wrapperSize: Size
): Triangle {
const sideCentralPoint = getCentralPoint(pos, vertexes)
// 计算底边长度
if (['top', 'bottom'].includes(pos)) {
const rate = pos === 'top'
? Math.abs(cp.y - sideCentralPoint.y) / cp.y
: Math.abs(cp.y - sideCentralPoint.y) / (wrapperSize.height - cp.y)
const lSideLength = Math.abs(cp.x - vertexes[0].x) / rate
const rSideLength = Math.abs(cp.x - vertexes[1].x) / rate
// 左侧点 x y
const lx = cp.x - lSideLength
const ly = pos === 'top' ? 0 : wrapperSize.height
// 右侧点 x y
const rx = rSideLength + cp.x
const ry = ly
return [
{ x: lx, y: ly },
{ x: rx, y: ry },
{ ...cp }
]
} else {
const rate = pos === 'right'
? Math.abs(cp.x - sideCentralPoint.x) / (wrapperSize.width - cp.x)
: Math.abs(cp.x - sideCentralPoint.x) / cp.x
const tSideLength = Math.abs(cp.y - vertexes[0].y) / rate
const bSideLength = Math.abs(cp.y - vertexes[2].y) / rate
// 上侧点 x y
const tx = pos === 'left' ? 0 : wrapperSize.width
const ty = cp.y - tSideLength
// 下侧点 x y
const bx = tx
const by = bSideLength + cp.y
return [
{ x: tx, y: ty },
{ x: bx, y: by },
{ ...cp }
]
}
}
export default (
rect: Ref<Rect>,
wrapperSize: Size
) => {
// 获取四个三角形
const triangles = computed(() => {
const {
translate: {
x,
y
},
width,
height,
allowPoints
} = rect.value
// 矩形四个顶点
// top-left top-right
// bottom-left bottom-right
const vertexes: RectVertexes = [
{ x, y },
{ x: x + width, y },
{ x, y: y + height },
{ x: x + width, y: y + height }
]
// 矩形中点
const cp: Point = {
x: x + width / 2,
y: y + height / 2
}
const triangles: Triangles = {
top: null,
right: null,
bottom: null,
left: null
}
allowPoints.forEach(pos => {
triangles[pos] = getTriangle(
pos,
vertexes,
cp,
wrapperSize
)
})
return triangles
})
return {
triangles
}
}
src/composables/useCurve.ts
ts
import { Ref, computed } from 'vue'
import { Rect } from '..'
export default (
rect1: Ref<Rect>,
rect2: Ref<Rect>
) => {
const x1 = computed(() => rect1.value.translate.x + rect1.value.point.x)
const y1 = computed(() => rect1.value.translate.y + rect1.value.point.y)
const x2 = computed(() => rect2.value.translate.x + rect2.value.point.x)
const y2 = computed(() => rect2.value.translate.y + rect2.value.point.y)
const cubicBezierCruve = computed(() => {
const cpx1 = x1.value + (x2.value - x1.value) / 2
const cpy1 = y1.value
const cpx2 = cpx1
const cpy2 = y2.value
return `
M ${x1.value} ${y1.value}
C ${cpx1} ${cpy1}, ${cpx2} ${cpy2}, ${x2.value} ${y2.value}
`
})
return {
path: cubicBezierCruve
}
}
src/utils/tools.ts
ts
import { Point, Triangle } from '..'
// 向量
const vec = (a: Point, b: Point): Point => {
return {
x: b.x - a.x,
y: b.y - a.y
}
}
// 叉乘函数
const vecProduct = (v1: Point, v2: Point) => v1.x * v2.y - v2.x * v1.y
const sameSymbols = (a: number, b: number) => (a ^ b) >= 0
/**
* 判断某个点是否在三角形内部
* 点位于三角形三条边的同一侧
* @param triangle
* @param point
*/
export const isPointInTriangle = (triangle: Triangle, point: Point) => {
const PA = vec(point, triangle[0])
const PB = vec(point, triangle[1])
const PC = vec(point, triangle[2])
const R1 = vecProduct(PA, PB)
const R2 = vecProduct(PB, PC)
const R3 = vecProduct(PC, PA)
return sameSymbols(R1, R2) && sameSymbols(R2, R3)
}
src/index.d.ts
ts
export interface Point {
x: number
y: number
}
export interface Size {
width: number
height: number
}
export interface Rect extends Size {
name: string
translate: Point
allowPoints: Array<'top' | 'right' | 'bottom' | 'left'>,
point: Point
}
type RectVertexes = [Point, Point, Point, Point]
export type Triangle = [Point, Point, Point]
export interface Triangles {
top: Triangle | null
right: Triangle | null
bottom: Triangle | null
left: Triangle | null
}
需要注意的是,这个 demo 里面对边缘计算没有过多涉及,如有需要请自行增加代码适配。
